|
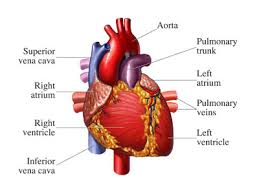
Heart
|
The chambered muscular organ that pumps blood received
from the veins into the arteries, thereby maintaining
the flow of blood through the entire circulatory system
to supply oxygen to the body. |
|
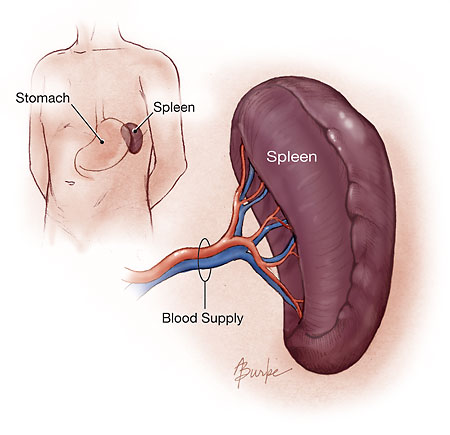
Spleen
|
The organ that is responsible for purifying the blood as
well as storing blood cells. |
|
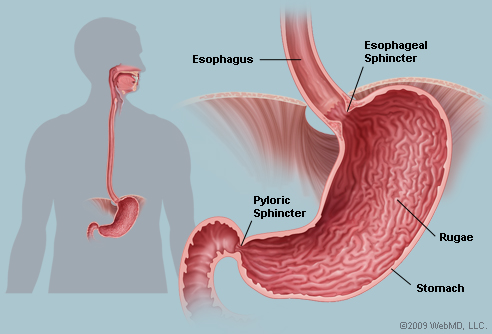
Stomach |
The enlarged, saclike canal, one of the principal organs
of digestion, located between the esophagus and the
small intestine. |
|
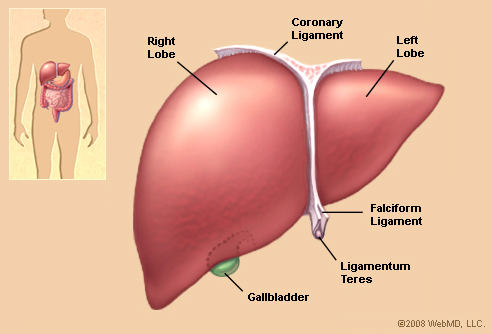
Liver |
A large, reddish-brown, organ located in the upper right
portion of the abdominal cavity that secretes bile and
is active in the formation of certain blood proteins and
in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
|
|
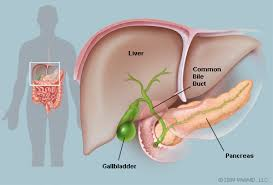
Gallbladder |
A small, pear-shaped muscular sac, located under the
right lobe of the liver, in which bile secreted by the
liver is stored until needed by the body for digestion. |
|
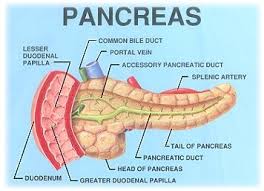
Pancreas |
A long, irregularly shaped gland in vertebrates, lying
behind the stomach, that secretes pancreatic juice into
the duodenum and insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin
into the bloodstream. |
|
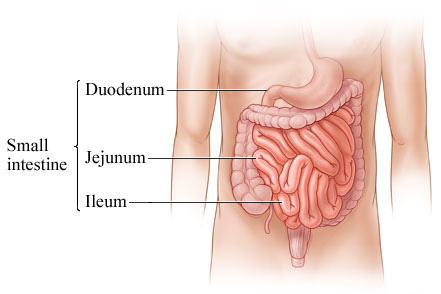
Small
Intestine |
The upper portion of the bowel, in which the process of
digestion is practically completed. It is narrow and
contorted, and consists of three parts, the duodenum,
jejunum, and ileum. |
|
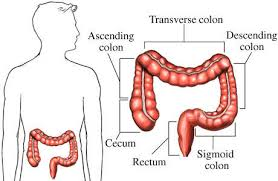
Large
Intestine |
Beginning with the cecum and ending with the rectum;
includes the cecum and the colon and the rectum;
extracts moisture from food residues which are later
excreted as feces |
|
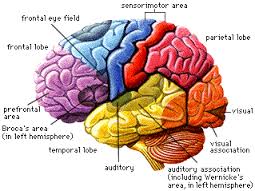
Brain |
The brain is the master control center of the body. It
receives information through the senses from inside and
outside of the body. It analyzes this information then
sends messages to the body that controls its functions
and actions. The brain remembers past experiences, is
the source of thought, moods, and emotions. |
|
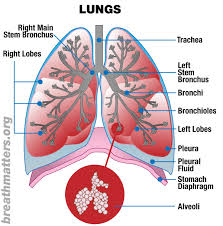
Lungs |
Either of two spongy, saclike respiratory organs in most
vertebrates, occupying the chest cavity together with
the heart and functioning to remove carbon dioxide from
the blood and provide it with oxygen. |
|
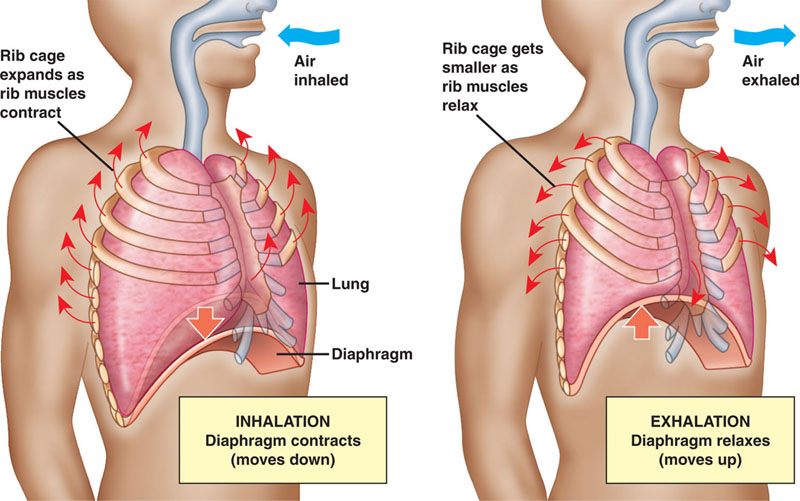
Diaphragm |
The main muscle used in the process of inspiration or
breathing in. It is a dome-shaped sheet of muscle that
is inserted into the lower ribs. |
|
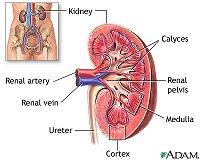
Kidneys |
A pair of organs functioning to maintain proper water
and electrolyte balance, regulate acid-base
concentration, and filter the blood of metabolic wastes,
which are then excreted as urine. |
|
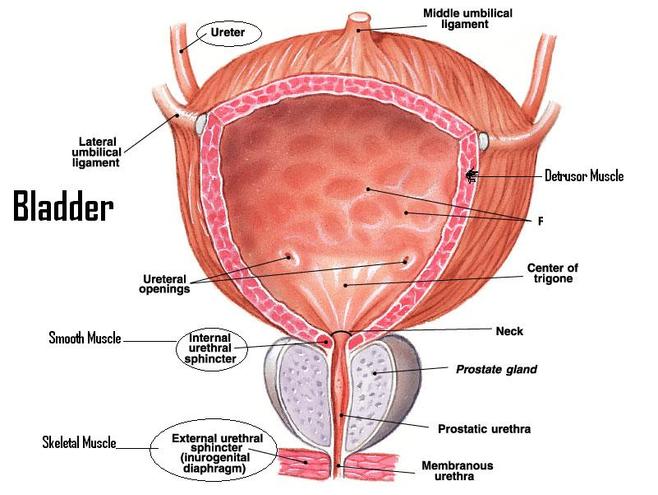
Bladder |
A hollow muscular organ that stores urine before
expelling it from the body. |