Conditional loops repeat as long as - or until - some condition is true. The following programming example illustrates how they work:
# A Name Guessing Game - similar to the Magic Number game
# The name that we are guessing
name = "George"
# Get the first guess and set numGuesses accordingly
guess = input("What\'s my name?")
numGuesses = 1
Repeat as long as your guess is wrong
while guess != name:
numGuesses = numGuesses + 1
print("No, it isn\'t ", guess, " but try again.")
guess = input("What\'s my name?")
# The player is finally right
print("YES! It IS ", name)
print("It took you ", numGuesses, " guesses.")
The flowchart will look very similar to what we drew when working with counting loops, but the decision is different:
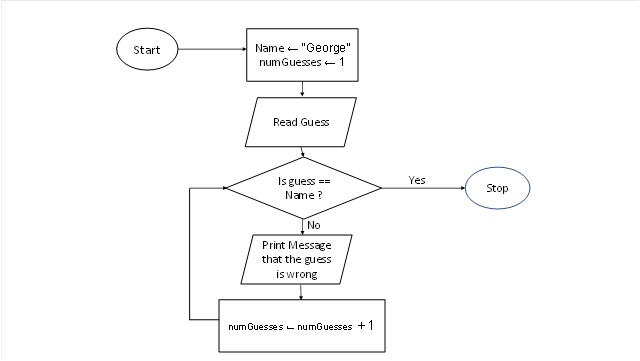
You will submit a flowchart, your pseudocode, and your Python program (properly commented).