Recursion Outline:
Recursive in English is a procedure
that can repeat a version of itself indefinitely – such as mirrors looking at
each other.
Recursion in Mathematics is:
defining an object in terms of itself:
Recursion in Java is a method that calls
itself (or calls something that then calls itself) repeatedly. In order not to
repeat forever, it needs to have a stopping point.
Factorials:
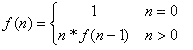
Fibonacci:
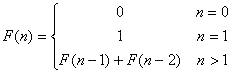
Snowflakes:
 (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Recursive_definition)
(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Recursive_definition)
A really good explanation is found
at: Amjad, Zeeshan.
"Recursion Primer Using C : Part 1." - CodeProject®. The Code Project, 22 Apr. 2008. Web. 19 Mar. 2012.
<http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/25470/Recursion-Primer-Using-C-Part-1>.
Excerpts
of Amjad’s article follow:
How does Recursion work?
Linear Recursion:
Factorials:
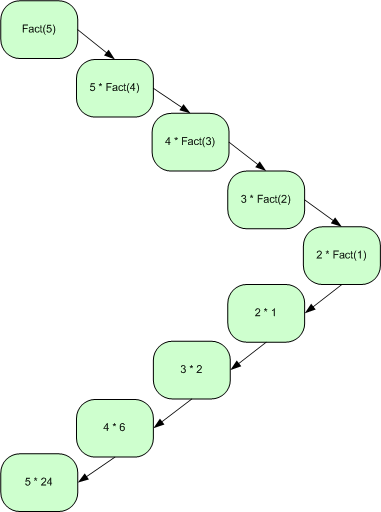
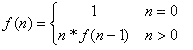
int
Factorial(int no)
{
// error
condition
if
(no < 0)
return -1;
// termination
condition
if
(0 == no)
return 1;
// linear
recursive call
return
no * Factorial(no - 1);
}
Fibonacci: Binary Recursion:
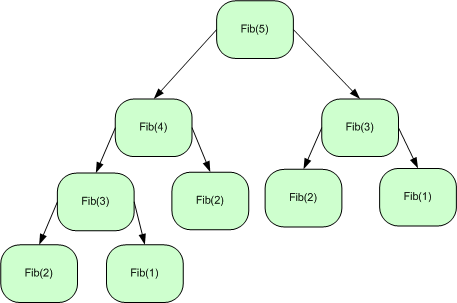
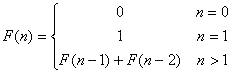
int
Fib(int no)
{
// error
condition
if
(no < 1)
return -1;
// termination
condition
if
(1 == no || 2
== no)
return 1;
// binary
recursive call
return
Fib(no - 1) + Fib(no - 2);
}
Now,
for a great non-number example, on to codingbat : http://codingbat.com/prob/p183174
nestParen
Given a
string, return true if it is a nesting of zero or more pairs of parenthesis,
like "(())" or "((()))". Suggestion: check the first and
last chars, and then recur on what's inside them.
nestParen("(())")
→ true
nestParen("((()))") → true
nestParen("(((x))") → false
Definition:
When the string is
empty, zero or
more pairs of parentheses is true
When the string is not
empty:
When the first and last
are ( and ), continue to check what is inside
When the first and last
are not ( and ), you know it fails.
Thinking about the header
- What does
this method need to know? -à the
letters being examined
- What does this
method need to return? à
true or false
- So what is
the header: public boolean nestParen(String
str)
How to code When
the string is empty,
zero or more pairs of parentheses is true
- Use an If
statement
- Determine
if the length is 0 using str.length() OR str == null
How to code When
the string is not empty and the first and last characters are ( and ) :
- Get the
first letter using str.charAt(0)
- Get the
last character using str.charAt(str.length()-1);
- Get the string
that starts with the second letter and cuts out the last letter using str.substring(1, str.length()-1);
- Recursively
check for the inside string to work
How to code When
the first and last are not ( and ), you know it fails.
- just return
false