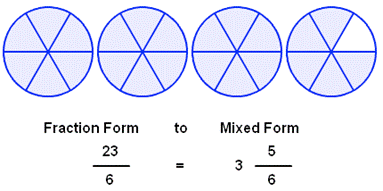
|
MST State Standards:
2.
Students use number sense and numeration to develop an understanding
of the multiple uses of numbers in the real world, the use of numbers to
communicate mathematically, and the use of numbers in the development of
mathematical ideas.
- Use whole numbers and fractions to identify locations, quantify
groups of objects, and measure distances.
- Use concrete materials to model numbers and number relationships
for whole numbers and common fractions, including decimal fractions.
4. Students
use mathematical modeling/multiple representation to provide a means of
presenting, interpreting, communicating, and connecting mathematical
information and relationships.
o
Construct
tables, charts, and graphs to display and analyze real-world data.
o Use multiple representations (simulations,
manipulative materials, pictures, and diagrams) as tools to explain the
operation of everyday procedures.
o Students
use physical materials, pictures, and diagrams to explain mathematical ideas
and processes and to demonstrate geometric concepts.
|
|
Integrated Standards:
- The Arts Standard 1: Creating, Performing, and Participating in the Arts
o Students
identify and use, in individual and group experiences, some of the roles and
means for designing, producing, and exhibiting art works.
|
|
Objectives: SWBA
to…
- Define
mixed number.
- Read
and write mixed numbers.
- Use
objects and pictures to show mixed numbers.
|
|
Aim:
- How
do we create a mixed number?
|
|
Materials:
- Smartboard
- Paper
plates
- Scissors
- Crayons
- Recording
notebook or paper
- Practice
worksheet
|
|
Assessment:
- Teacher
will observe and ask questions of each group to see if they can show a
fractional part and a mixed number with their paper plates. Have
students complete a worksheet to see if they can recognize fractional
parts and mixed numbers. You can use the worksheet described above or
use another that requires students to recognize both simple and mixed
fractions.
|
|
Procedure:
- As
a pre-activity, the teacher will generate a discussion by asking
students, “What does it means to mix something?” Students will give responses, and
then the teacher will ask, “What is a mixed number?”
- The
teacher will use the smartboard to produce circles and rectangles to
demonstrate two or more whole numbers.
One whole will then be divided into two equal parts, three
equal parts, etc. The class
will discuss different combinations of more than 1 circle with parts
of another circle.
- After
the pre-activities, the teacher will distribute scissors, crayons, and
one paper plate to each student.
Students will be instructed to take a couple minutes to quickly
add some color to their plates.
- Once
colored, the teacher will demonstrate and instruct students to fold
their paper plate in half, and then cut it into two equal parts. Have them discuss, pull apart and
put together, to demonstrate the whole and the two parts making up the
whole.
- The
teacher will demonstrate and have students fold each half into two
equal parts. Have them cut on the fold and cut into four parts. Again,
discuss the whole and the parts, manipulating the pieces to show the
whole and then the parts.
- While
working with the members of your table/desk formations, the teacher
will give the students whole paper plates with their plates that they
have cut into parts. Have students will manipulate the plates and
parts to show different mixed numbers to show the other groups.
Students will manipulate as many mixed number combinations as
possible, and record them all in their notebooks.
- After
about 10-15 minutes, depending on the rate of the students, the
teacher will ask group members to come up to the front of the class to
write their mixed number and the board and demonstrate it with the
plates.
|
|
|
Key Questions:
- What
does it mean to mix?
- What
is a mixed number?
- Can
a mixed number be less than 1?
|
|
Adaptations for Special Need & enrichment
differentiation:
- The
teacher’s demonstration will help those students that do not understand
how to fold their plates equally.
Peer help is also encouraged during the folding and cutting
process. However, students are
not to simply do it for another peer.
- If
groups have trouble working together, the teacher can assign each
student a specific job such as one to manipulate, one to record, one to
color, etc.
|
|
Follow-up Assignments
·
For more practice, students will have a
worksheet in which they will need to work in the opposite direction with
mixed numbers. Instead of starting
with a picture or plates, students will be given a fraction and then asked to
draw a picture to represent each fraction.
|
|
Reflection and Revision:
·
I have taught a mixed number lesson, however,
it did not follow this plan. I
originally used slices of bread, whole and fractional slices, to demonstrate
mixed numbers. Neither myself, nor my
students were successful with the procedure.
I then changed my demonstration and used pictures on the smartboard,
which really seemed to help students understand mixed numbers. Therefore, I have written this lesson plan
and have made use of pictures as the initial demonstration, and then switched
to use objects later in the lesson.
|