
Introduction | The Task | Resources | Evaluation | Learning Standards | Conclusion
| Forest Desert Prairie/Grassland Tundra Aquatic environmental issues |
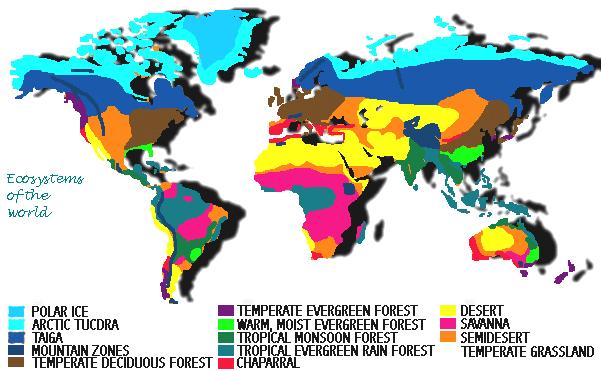
IntroductionThe
biosphere is divided into six major land biomes: Tundra, Taiga
(coniferous
forest), Deciduous Forest, Grasslands, Deserts, and Tropical Rain
Forests. In addition there are two water biomes - the
Marine biome,
which includes all the oceans and seas of the world and the Freshwater
biome. |

You are the
newly
appointed Deputy
Secretary of the Office of International Affairs, Department of the
Interior
(http://www.doi.gov/intl/)
for
President Barack Obama. The
U.S. Department of the Interior (DOI) is the primary conservation
agency of the
United States whose function is to maintain our country’s natural
resources. Their Office of International
Affairs is responsible for fulfilling international
treaty obligations
that
deal with endangered species, wetlands, the protection of world
cultural and
natural heritage, and marine pollution, and providing technical
assistance and
scientific advice on wildlife, water, and other natural resources
(e.g., water
issues in Middle East peace talks), park management, and addressing
environmental hazards (e.g., volcano and earthquake monitoring).
http://pnt.gov/membership/doi.shtml
The
President is embarking on a worldwide tour of diverse biomes.
Since he is such a busy man, he needs you to provide
him with a dossier (a file
containing detailed records on a particular subject) on
the biomes he is scheduled to visit. You
must provide him with background
information on the biome as well as any environmental issues concerning
the biome. The President wants to know if there is anything
that can be done to curtail these problems in the future. Be sure
to give him some of your ideas. You and your staff will separate
into five research teams and each team will research one of the
following biomes: Forest
(Temperate Deciduous and Rainforest), Desert,
Prairie/Grassland, Tundra, Aquatic
(Ocean and Freshwater - lakes and rivers.) You may present this information
in the format that you find most effective whether it is a poster, a
report, a scrapbook, a brochure, a powerpoint presentation, or
some other method. You
must also present your findings to the President and members of
Congress, providing each with a one
page summary.
|
|
|
Points |
|
Describe
the biome’s physical make-up. |
20 |
|
|
1.
Topography (mountains, hills, major rivers, lakes, and etc.) |
|
|
|
Describe
at least three plants found in the biome. |
20 |
|
|
1.
Describe three plants stating characteristics and adaptations of each. |
|
|
|
Extra
points for pictures of each plant included. If a picture of each
plant is included place the common and scientific name above each
picture. |
|
|
|
Describe
at least two animals found within the biome. |
20 |
|
|
1.
Describe five animals stating characteristics and adaptations of each. How do the adaptations allow each animal to
survive in this biome |
|
|
|
2. Include
the common and scientific name of each animal. |
|
|
|
Extra
points for pictures of each animal included. If a picture of each
animal is included place the common and scientific name above each
picture. |
|
|
|
Discuss
and explain the food web. |
20 |
|
|
5 plants |
|
|
|
3 animals |
|
|
|
Not all
carnivores |
|
|
|
Creativity
and presentation (neatness, use of color, punctuation, grammar, etc.) |
20 |
|
|
TOTAL
POINTS |
100 |
|
|
Beginning 1 |
Developing 2 |
Accomplished 3 |
Exemplary 4 |
Score |
|
|
|
Not
sure of what your position is. Little or no supporting details. |
Definite
knowledge of position but few supporting details. |
Definite
knowledge of position with sufficient supporting details and a mix of
general and specific examples. |
Excellent
knowledge of position citing mostly specific examples in defense of
your position. |
|
|
|
Little
or no interpretation of data. |
Interpretation
of data is minimally developed and utilizes few supporting details. |
Interpretation
of data is well developed with adequate use of specific details. |
Interpretation
of data demonstrates a thorough understanding of the issue and its
consequences and is supported by relevant specific details. |
|
|
|
Very
frequent errors which make the writing difficult to understand. |
Frequent
errors which make the writing difficult to understand. |
Errors
do not detract from understanding the writing. |
Errors
are infrequent, and writing is clear. |
|
|
|
Rarely
cooperates with team. |
Occasionally
cooperates with team. |
Usually
cooperates with team. |
Almost
always cooperates with team. |
|
|
|
Information
was read rather than presented and/or ideas not successfully conveyed
to audience. |
A
combination of reading and presenting of information was used and/or
ideas minimally conveyed to audience. |
Most
information was presented rather than read and ideas clearly conveyed
to audience. |
Strong
presentation and outstanding communication of ideas to audience. |
|
|
Visual |
No
visual, visual does not support your stance or visual is unappealing. |
Visual
is somewhat supportive of your stance but can be more visually
appealing. |
Visual
is effective and does support your stance. |
Excellent
visual that completely supports your stance. |
|
|
Summary
Handout |
Inadequate
information supplied. |
Some
information provided but not clearly explained. |
Research
explained in detail in clearly understandable language. |
Thoroughly
researched and meticulously compiled. Comprehensive
yet succinct. |
|
GRADE BASED ON POINTS EARNED: A: 23 - 28
B:
22 - 17
C:
16 - 11
D:
10 – 6
F:
<6
Intermediate
Science – NYS Learning Standards
The Living Environment
5.1d
The methods for obtaining nutrients vary
among organisms. Producers, such as green plants, use light energy to
make
their food. Consumers, such as animals, take in energy-rich foods.
5.1e
Herbivores obtain energy from plants.
Carnivores obtain energy from animals.
Omnivores obtain energy from both plants
and animals. Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, obtain energy by
consuming wastes and/or dead organisms.
5.1g
The survival of an organism depends on its
ability to sense and respond to its external environment.
6.1a
Energy flows through ecosystems in one
direction, usually from the Sun, through producers to consumers and
then to
decomposers. This process may be visualized with food chains or energy
pyramids.
6.1b
Food webs identify feeding relationships
among producers, consumers, and decomposers in an ecosystem.
6.1c
Matter is transferred from one organism to
another and between organisms and their physical environment. Water,
nitrogen,
carbon dioxide, and oxygen are examples of substances cycled between
the living
and nonliving environment.
7.1a
A population consists of all individuals of
a species that are found together at a given place and time.
Populations living
in one place form a community. The community and the physical factors
with
which it interacts compose an ecosystem.
7.1b
Given adequate resources and no disease or
predators, populations (including humans) increase. Lack of resources,
habitat
destruction, and other factors such as predation and climate limit the
growth
of certain populations in the ecosystem.
7.1c
In all environments, organisms interact
with one another in many ways. Relationships among organisms may be
competitive, harmful, or beneficial. Some species have adapted to be
dependent
upon each other with the result that neither could survive without the
other.
7.1e
The environment may contain dangerous
levels of substances (pollutants) that are harmful to organisms.
Therefore, the
good health of environments and individuals requires the monitoring of
soil,
air, and water, and taking steps to keep them safe. Describe the
effects of
environmental changes on humans and other populations.
7.2a
In ecosystems, balance is the result of
interactions between community members and their environment.
7.2b
The environment may be altered through the
activities of organisms. Alterations are sometimes abrupt. Some species
may
replace others over time, resulting in longterm gradual changes
(ecological
succession).
7.2c
Overpopulation by any species impacts the
environment due to the increased use of resources. Human activities can
bring
about environmental degradation through resource acquisition, urban
growth,
land-use decisions, waste disposal, etc.
7.2d
Since the Industrial Revolution, human
activities have resulted in major pollution of air, water, and soil.
Pollution
has cumulative ecological effects such as acid rain, global warming, or
ozone
depletion. The survival of living things on our planet depends on the
conservation and protection of Earth’s resources.
English
Language Arts – NYS Learning Standards
1.1.
Listening and reading to acquire
information and understanding involves collecting data, facts, and
ideas;
discovering relationships, concepts, and generalizations; and using
knowledge
from oral, written, and electronic sources.
1.2.
Speaking and writing to acquire and
transmit information requires asking probing and clarifying questions,
interpreting information in one’s own words, applying information from
one
context to another, and presenting the information and interpretation
clearly,
concisely, and comprehensibly.
ch
Technology
Learning Standards:
2.1
Information
technology is used to retrieve, process, and communicate information
and as a
tool to enhance learning.
2.3
Information
technology can have positive
and negative impacts on society, depending upon how it is used.
6.2. Models are
simplified representations of objects, structures, or systems used in
analysis,
explanation, interpretation, or design.
7.1. The knowledge
and skills of mathematics,
science, and technology are used together to make informed decisions
and solve
problems, especially those relating to
issues of
science/technology/society, consumer decision making, design, and
inquiry into
phenomena.
7.2.
Solving
interdisciplinary problems
involves a variety of skills and strategies, including effective work
habits;
gathering and processing information; generating and analyzing ideas;
realizing
ideas; making connections among the common themes of mathematics,
science, and
technology; and presenting results
Great
job!! You have successfully provided our
Commander in Chief with all of the information that he needs to
effectively
complete his journey. Your information on
environmental issues regarding your assigned biome was clear and
concise and
brought all of the pertinent issues to his attention.
Your hard work and efforts have succeeded in shining
a light on the important issues that need to be addressed.
By
listening to your colleague’s presentations, you have become aware of
all other
biomes - you should now be aware of the different plants and animals in
them,
the varying climates, how biotic and abiotic things positively and
negatively
affect the environment, and how we can help. You have raised
awareness about the ecological
concerns and conservation efforts in various areas and can take the
necessary
steps to ensure their continued existence.




 http://www.kidsgeo.com/images/tundra.jpg
http://ecoworldly.com/category/south-america/brazil/
http://www.xanaduranchgetaway.com/
http://creationontheblade.blogspot.com/2007/04/words-of-water.html
http://aqua-ca.com/coralreef.aspx
http://www.kidsgeo.com/images/tundra.jpg
http://ecoworldly.com/category/south-america/brazil/
http://www.xanaduranchgetaway.com/
http://creationontheblade.blogspot.com/2007/04/words-of-water.html
http://aqua-ca.com/coralreef.aspx